Adding FHIR metadata¶
Background¶
Adding files to a project is a two-step process:
- Adding file metadata entries to the manifest (see adding files)
- Creating FHIR-compliant metadata using the manifest
This page will guide you through the second step of generating FHIR metadata in your g3t project. To understand the FHIR data model, see FHIR for Researchers
Generating FHIR Data using g3t¶
To submit metadata from the manifest to the platform, that metadata needs to be converted into FHIR standard. We will use the file metadata entries we had created during the g3t add on our data files.
Creating metadata files using the manifest¶
Using the file metadata entries created by the g3t add command, g3t meta init creates FHIR-compliant metadata files in the META/ directory, where each file corresponds to a FHIR resource. At a minimum, this directory will create:
| File | Contents |
|---|---|
| ResearchStudy.ndjson | Description of the project |
| DocumentReference.ndjson | File information |
Depending on if a patient or specimen flag was specified, other resources can be added to the metadata files:
- subjects (ResearchSubject, Patient)
- specimens (Specimen)
- assays (Task)
-
measurements (Observation)
-
This command will create a skeleton metadata file for each file added to the project using the
patient,specimen,task, and/orobservationflags specified by theg3t addcommand. - You can edit the metadata to map additional fields.
- The metadata files can be created at any time, but the system will validate them before the changes are committed.
- Note: If an existing file is modified, it won't get automatically staged
- For instance, if
DocumentReference.jsonis already created and it has to be updated to reflect an additional file, this change is not automatically staged. - Make sure to either
git add META/or use the-aflag ing3t committo ensure that your FHIR metadata changes are staged.
Example¶
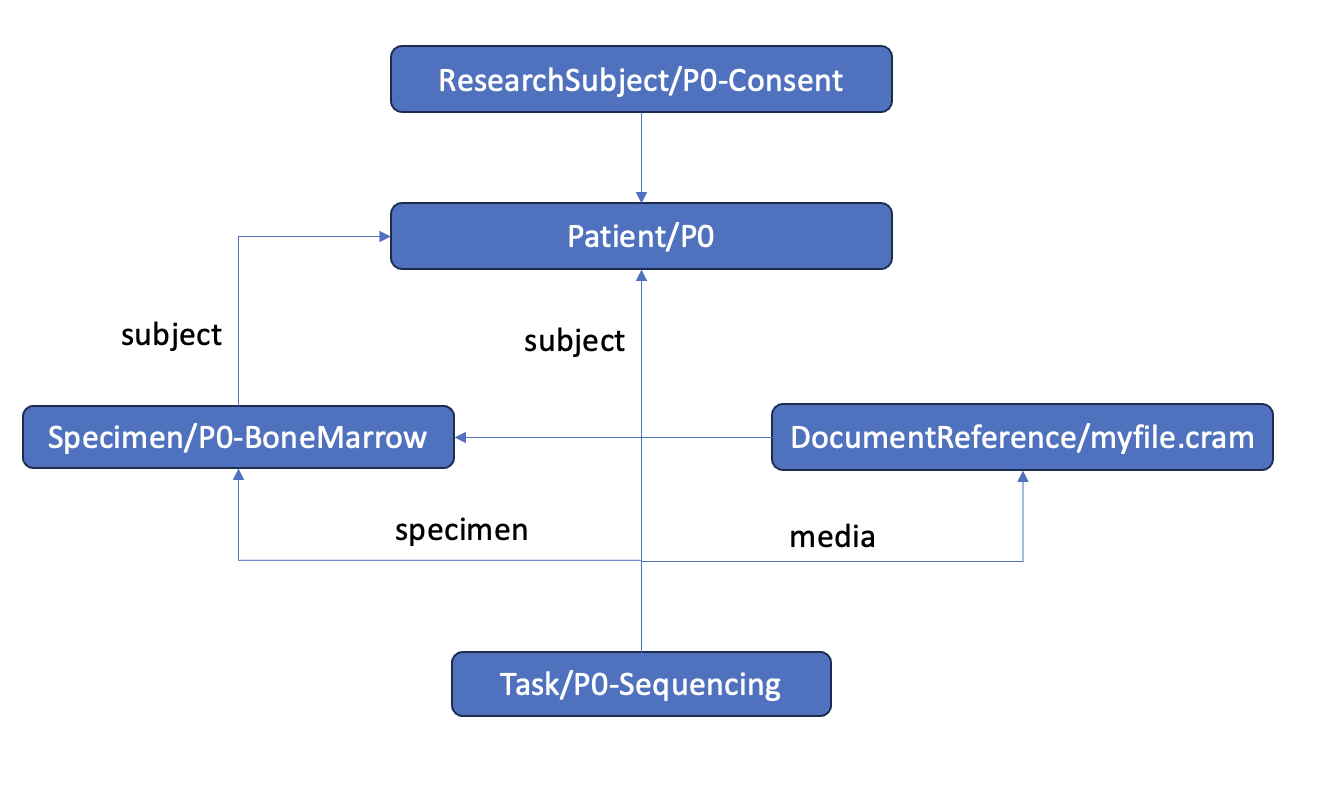
To add a cram file that's associated with a subject, sample, and particular task
This will produce metadata with the following relationships:
When the project is committed, the system will validate new or changed records. You may validate the metadata on demand by:
$ g3t meta validate --help
Usage: g3t meta validate [OPTIONS] DIRECTORY
Validate FHIR data in DIRECTORY.
Rationale for the META directory¶
All FHIR metadata is housed in the META/ directory. The convention of using a META directory for supporting files is common practice in data management. This directory is used to organize and store the metadata files of your project that describe the Study, Subjects, Specimens, Documents, etc. Here's a brief explanation of this convention:
- Separation of concerns: The
METAdirectory provides a clear separation between your metadata and other project files. This helps maintain a clean and organized project structure. - Clarity and Readability: By placing metadata files in a dedicated directory, it becomes easier for researchers (including yourself and others) to locate and understand the main codebase. This improves overall project clarity and readability.
- Build Tools Integration: Many build tools and development environments are configured by default to recognize the
METAdirectory as the main metadata location. This convention simplifies the configuration process and ensures that tools can easily identify and analyze your data files. - Consistency Across Projects: Adopting a common convention, such as using
METAfor metadata files, promotes consistency across different projects. When researchers work on multiple projects, having a consistent structure makes it easier to navigate and understand each study. - The 'META' directory will contain a file per FHIR resource with the extension .ndjson. e.g.
ResearchStudy.ndjson
Supplying your own FHIR metadata¶
In some cases, it might be useful to supply your own FHIR metadata without using g3t add to create any file metadata. In that case, adding metadata would take on the following flow:
- Initialize your project
- Copy external FHIR data as
.ndjsonfiles to yourMETA/directory git add META/g3t commit -m "supplying FHIR metadata"
This process would be useful for individuals who want to use the system to track relations between metadata but might not necessarily want to connect their actual data files to the system.
Next Steps¶
- See the tabular metadata section for more information on working with metadata.
- See the commit and push section for more information on publishing.